Key Takeaways
- Critical thinking skills are important for decision-making, problem-solving, creative thinking, and self-reflection.
- You can improve your critical thinking skills by asking open-ended questions, practicing problem-solving strategies, and challenging your assumptions and thinking.
- Individuals may subconsciously use critical thinking skills in everyday life, such as solving problems at work, researching at university, or weighing options for personal decision-making.
As a term, critical thinking originates from the mid-late 20th century. It is the process of analyzing, assessing, and synthesizing data to reach logical conclusions. This 21st-century skill helps individuals approach each challenge with clarity and reasoning. Critical thinking also develops intellectual independence and the ability to make informed decisions.
Wondering how to develop your critical thinking skills? This blog is here to guide you step by step through the process.
Why Are Critical Thinking Skills Important?
Critical thinking skills play an important role in making informed decisions, solving complex problems, and improving communication skills. These skills encourage you to analyze situations, navigate challenges, and be more open to different perspectives. Critical thinking primarily focuses on making judgments with clarity, logic, and evidence rather than with emotions or assumptions.
According to a report by The World Economic Forum, critical thinking and creativity are two of the most important skills that the labor market requires. Critical thinking greatly enhances your capacity for creative thought by enabling you to see issues from a wider perspective, generate unconventional ideas or solutions, and carry out creative plans.
Furthermore, critical thinking is applicable and required for all fields, regardless of the career or path you choose.
How to Develop Critical Thinking Skills

Critical thinking is vital in every professional field and can be developed through daily practices like asking thought-provoking questions, exploring diverse perspectives, solving problems, self-reflecting, and challenging assumptions. Let’s explore each of these practices in more detail:
Ask thought-provoking questions
You can develop critical thinking by asking open-ended and probing questions, which help you reflect and understand situations better. As a skilled critical thinker, you challenge what you know and ask questions to evaluate the information that others give you.
You can achieve this by asking questions that focus on understanding all aspects of the argument or problem before making judgments. Remind yourself to think of the goal you are trying to reach so that you can ask the right questions. You can develop critical thinking skills and stop taking things at face value by asking questions like “Why is this a problem?” and “How can we approach this problem with clarity?”
Consider different perspectives
Another key step is cultivating the ability to embrace new ideas, consider opposing perspectives, or remain open to feedback. This encourages you to critically evaluate information and arguments that help you recognize any potential biases or misconceptions. By engaging with diverse viewpoints, you can expand your understanding, enhance your creativity, and refine your decision-making skills. Taking into account a lot of different aspects of a particular situation helps you succeed as a student and in your future endeavors in general.
Practice problem-solving
Problem-solving can be improved by designing a structured approach to analyzing situations, weighing options, and implementing plans. This process builds the strength, adaptability, and agility to manage complex issues with more confidence and accuracy.
Key aspects of problem-solving include the four P’s: problem, plan, people, and process. Individuals first identify problems, then design a plan, specify the people involved, and finally start with the improvement process. Although problem-solving may take additional steps, these core principles enable you to practice and achieve successful outcomes in this skill.
Reflect on your thinking process
To improve your critical thinking abilities, you must reflect on how you think. Through this practice, you can recognize weaknesses, biases, or false assumptions that may cloud your judgment. In addition, reflection fosters self-awareness, improves your intellect, and helps you make better decisions.
Incorporate reflection into your daily routine by asking yourself questions, journaling, or seeking support from friends and family. These strategies help you change any behaviors that may hinder your success.
Challenge assumptions
Critical thinkers consistently challenge their own assumptions to sharpen their logic and uncover any potential biases. They first identify any beliefs they take for granted and question where they originated from. For instance, asking, “What is the evidence to prove this is true?” or “What if the opposite were true?”. This practice can clarify their decisions further and develop an objective understanding of complex issues.
Critical thinkers also engage in discussions that challenge their views and help them reflect on whether personal experiences or societal norms affect their thinking.
Examples of Critical Thinking in Everyday Life
Critical thinking is present in our everyday lives and situations. Whether solving problems in the workplace, conducting research, or developing plans in education, critical thinking empowers people to make informed decisions and approach challenges with clarity and precision.
Critical thinking in the workplace
Critical thinking is essential for solving problems, making informed decisions, and optimizing processes in the workplace. A recent report from an employer survey of 501 business executives revealed that 78% of employers recognize critical thinking as the most important skill in their employees.
For example, a project manager uses critical thinking to analyze project risks, assess potential solutions, and choose the most productive strategy to secure deliveries on time. Likewise, during team meetings, critical thinking helps employees explore different approaches to create innovative solutions.
Moreover, private businesses need critical thinking to develop strategies that attract customers and improve their services or to design innovative products.
Critical thinking in education
Students use and develop critical thinking in education to evaluate the credibility of sources, analyze arguments, and solve problems. For instance, students write research papers by checking the validity of sources and organizing their research logically and cohesively to build strong arguments.
On the other hand, professors also promote critical thinking by fostering classroom discussions that encourage students to think critically and be open to new ideas. Developing critical thinking abilities in students is also essential for them to succeed in their jobs and make better career decisions.
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. We will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours.
If there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:
- We value your privacy.
Critical thinking in personal decision-making
In daily life, critical thinking helps you make thoughtful and rational judgments. Depending on the decision—a financial investment, career path, or conflict resolution—critical thinking helps you weigh your options, consider any potential outcomes or risks, and make decisions based on reason rather than emotions or biases.
For example, personal decision-making scenarios like changing your job can benefit from critical thinking. By evaluating your current job satisfaction, exploring new opportunities that align with your interests and skills, and considering your long-term financial goals, you can make an informed and thoughtful decision.
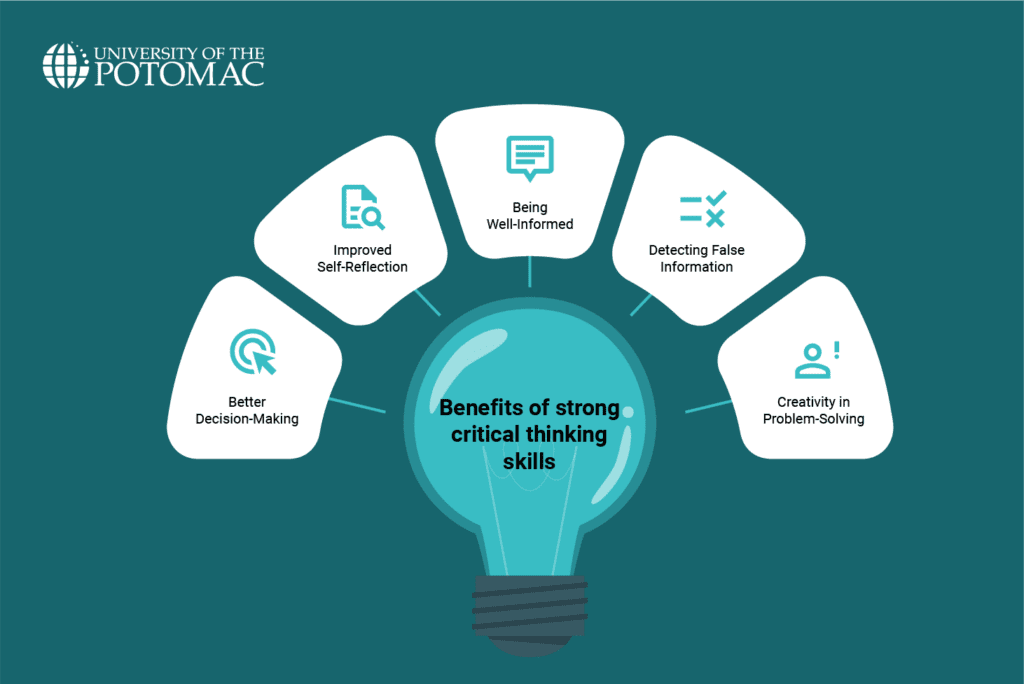
Benefits of Strong Critical Thinking Skills
As mentioned throughout this blog, strong critical thinking skills extend further beyond the scope of academia. They are significant to both personal, professional, and societal growth and contributions. Individuals with strong critical thinking skills approach difficult decisions with clarity, focus, and confidence.
In addition, these skills contribute to better communication—with individuals thinking clearly, expressing themselves logically, and understanding that different viewpoints don’t necessarily threaten their beliefs. Apart from that, critical thinking builds your resilience and adaptability when faced with uncertain and changing environments.
Some of the key benefits of strong critical thinking skills include:
- Better Decision-Making: Critical thinkers use logic, reasoning, and creativity when making decisions. When making decisions, they search for evidence, consider all of their options, and foresee any issues or worries that might arise. People must make responsible decisions, particularly as adults, so critical thinking should play a significant role in their daily lives.
- Improved Self-Reflection: Critical thinking helps you become more aware of your surroundings, beliefs, thoughts, and actions. You are more likely to recognize your own biases and limitations through self-reflection. This allows you to continually improve your knowledge, skills, or thinking patterns.
- Being Well-Informed: Critical thinkers are never afraid of learning more about their work or field of study. They are well informed, as they actively seek different information sources to have a better understanding of complex issues. This encourages them to discuss and contribute to the communities.
- Detecting False Information: Critical thinkers can identify any false information or not accept information at face value since they analyze and verify data.
- Creativity in Problem-Solving: Critical thinking skills help you apply creativity to various problems or situations. Individuals explore unconventional ideas and consider different approaches to solving problems or designing solutions.
Conclusion
Critical thinking skills remain significant to every career path or degree program. Critical thinkers are encouraged to approach complex problems with innovation, open-mindedness, and reasoning. They continually ask questions that focus on receiving clear and verified information from all perspectives without making assumptions or biases.
Critical thinking skills strengthen your relationships with people in the workplace, education systems, or personal life by allowing you to communicate clearly and effectively.
Individuals who want to develop critical thinking can adopt daily practices such as asking more open-ended questions, applying innovative thinking to solve problems, practicing reflective thinking, and challenging any possible assumptions or biases. They strengthen their adaptability, creative thinking, resilience, and communication skills.
Developing critical thinking skills is essential for success in the job market. Enroll in University of the Potomac programs now to begin cultivating, refining, and applying critical thinking abilities for a better future.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do critical thinking skills differ from creative thinking?
Critical thinking skills allow you to make reasoned judgments by analyzing data or evidence, while creative thinking is the ability to generate new ideas or solutions by thinking outside the box.
Can critical thinking be taught at any age?
Critical thinking is a skill that can be acquired when logical reasoning starts to develop, approximately between ages 7 and 10.