Data shows that it takes an average of 277 days to identify and contain a breach—207 days to identify it and another 70 days to contain it. This alarming statistic highlights the importance of organizations and cybersecurity teams working harder to secure their data. To help reduce this timeframe and enhance their defenses, cybersecurity professionals must possess specific skills that enable them to stay ahead of breaches and prevent them altogether.
Whether you’re just getting started in cybersecurity or are a seasoned professional looking to enhance your skill set, read on to discover some of the most important cybersecurity skills needed for a successful career in this field.
What Is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the field centered on defending computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from malicious attacks. Its primary objectives are to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information and assets. Therefore, cybersecurity focuses on three main principles: protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, ensuring data is accurate and trustworthy, and making sure that information and systems are available to authorized users when needed.
The scope of cybersecurity is broad, encompassing network security, application security, information security, and operational security. By addressing these areas, cybersecurity aims to create a defense against a wide range of cyber threats, ensuring the protection and reliability of an organization’s digital infrastructure.
What Does a Cybersecurity Specialist Do?
A cybersecurity specialist is responsible for protecting systems and networks from cyber threats and ensuring the security of sensitive data. Their key responsibilities include:
- Continuously observing network traffic to detect and respond to security breaches;
- Installing and maintaining firewalls, encryption, and other security tools to protect against attacks;
- Regularly testing systems and networks for weaknesses and implementing solutions to address identified vulnerabilities;
- Enforcing policies and procedures to ensure the organization follows best practices in information security;
- Quickly responding to and managing security incidents to minimize damage and recover from breaches;
- Educating staff on security protocols and practices to prevent breaches due to human error;
- Keeping up-to-date with the latest cybersecurity advancements and trends.
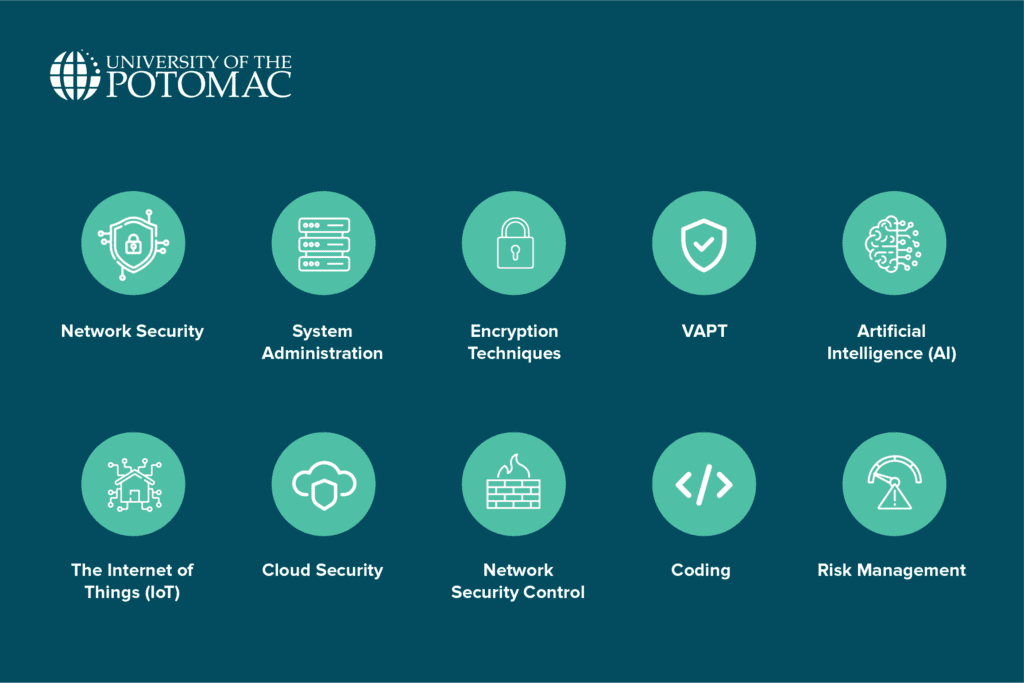
10 Essential Cybersecurity Skills You Must Have
In addition to the extensive theoretical knowledge required to understand the intricacies of network security, threat analysis, and data protection protocols, cybersecurity professionals also need practical skills to safeguard digital environments. The following are some of the most crucial cybersecurity skills every expert in the field must possess to excel.
1. Network security
Network security typically includes configuring and managing firewalls, deploying intrusion detection systems (IDS), and practicing network segmentation to isolate parts of the network that handle sensitive information. Virtual private networks (VPNs), anti-virus software, and anti-malware programs are also integral to maintaining this security.
Mastery of this skill is crucial for cybersecurity professionals because it enables them to design and enforce the security posture of the network. For instance, during a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack, professionals with network security expertise can quickly analyze the type of attack, identify the source, and implement rules to mitigate the attack by filtering or redirecting malicious traffic.
2. System administration
System administration skills encompass a wide range of functions focused on properly managing and securing the configurations of operating systems, servers, and other critical IT infrastructure components. These skills enable professionals to perform patch management, which involves regularly updating software to fix security holes before attackers can exploit them.
This proactive management of system configurations can reduce the potential for security breaches and ensure continuous system integrity and availability.
3. Encryption techniques
Some common encryption methods include symmetric-key encryption, asymmetric-key encryption, and hashing. Cybersecurity professionals use these techniques to implement secure communication protocols like HTTPS and secure file storage solutions.
Through such skills, cybersecurity professionals ensure that encrypted data remains safe because if an attacker gains access to an encrypted database, they cannot read the information without decrypting it. This significantly reduces the impact of a breach by protecting sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure.
4. Vulnerability assessment and penetration testing (VAPT)
VAPT are complementary techniques used to identify and resolve security vulnerabilities. Vulnerability assessment involves scanning systems and applications to detect known security weaknesses. In contrast, penetration testing (or pen testing) involves actively exploiting these weaknesses in a controlled environment to understand the potential impact of an attack. These assessments are crucial for maintaining system security over time and adjusting defenses as new threats emerge.
So, during a penetration test, a cybersecurity professional might discover that an outdated web server is vulnerable to SQL injection attacks. By simulating the attack, they can demonstrate the potential damage and ensure that appropriate fixes, such as input validation and parameterized queries, are implemented.
5. Artificial intelligence (AI)
AI significantly amplifies the effectiveness of cybersecurity teams by automating complex and time-consuming tasks. For instance, AI-driven systems can continuously monitor network traffic to detect anomalies that suggest potential security breaches, such as unusual access patterns or large data transfers at odd hours.
Furthermore, AI can detect zero-day exploits by recognizing and responding to unusual behavior patterns even when attack signatures are not previously known. Therefore, skills in working with such systems allow cybersecurity professionals to rapidly contain and mitigate various threats.
6. The internet of things (IoT)
Given the diversity and quantity of IoT devices, which range from simple sensors to complex controllers, each device can present unique security challenges. Security measures must, therefore, be tailored to individual device capabilities and the specific data they handle.
A cybersecurity professional with strong IoT security skills can safeguard devices by implementing standardized security protocols across the board, ensuring consistent security practices at every level. For example, by securing a network of smart industrial sensors, a cybersecurity professional can prevent scenarios where compromised devices could lead to production sabotage or safety hazards.
7. Cloud security
Cloud security is the discipline of protecting cloud-based systems, data, and infrastructure from a range of cyber threats. It typically involves mastering cloud architectures, implementing data encryption, and managing access through identity and access management systems.
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. We will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours.
If there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:
- We value your privacy.
Cybersecurity professionals with these skills can design and implement security measures that protect cloud environments while complying with industry standards and regulations. They can enforce data encryption at rest and in transit and set up stringent access controls that ensure only authorized users can access sensitive information in the cloud. This helps prevent data breaches and helps organizations leverage the benefits of cloud computing securely.
8. Network security control
Mastery of network security controls is essential for defending an organization’s digital boundaries. This involves deploying various protective measures, such as firewalls, intrusion prevention systems (IPS), intrusion detection systems (IDS), and access controls.
For instance, cybersecurity professionals can utilize firewalls to create a barrier between secure internal networks and potentially unsecured external networks. By correctly configuring and updating these firewalls, professionals can allow legitimate business traffic while blocking malicious or unnecessary traffic.
9. Coding
Secure coding skills are vital because they minimize software vulnerabilities during the development phase rather than after deployment. A cybersecurity professional with secure coding skills can ensure that any user-generated input is thoroughly checked before processing, thereby preventing SQL injections and XSS attacks, among other things.
These preventative measures save resources and enhance the security of applications by embedding defense mechanisms at the code level.
10. Risk management
Risk management in cybersecurity involves identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing risks, followed by coordinated efforts to minimize, monitor, and control the probability or impact of unfortunate events. This skill set requires understanding potential security threats, evaluating their impact on operations, and implementing appropriate strategies to mitigate these risks.
Effective risk management allows cybersecurity professionals to allocate their resources more effectively, focusing on the most significant risks to the organization. This strategic focus helps organizations maintain operational continuity, comply with legal and regulatory standards, and protect sensitive customer and company data, ultimately safeguarding the organization’s reputation and financial stability.
The Bottom Line
All in all, the skills highlighted in this article are crucial for the success of cybersecurity professionals. As the interconnected systems that make up the digital world continue to evolve, formal education remains a reliable pathway for acquiring these skills, as well as the theoretical knowledge demanded by the cybersecurity field.
Potomac’s Bachelor of Science in Cybersecurity is an excellent choice for gaining this expertise. With a carefully planned curriculum, the program equips and empowers you to effectively protect and secure digital environments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which cybersecurity skills are in the highest demand?
Cloud computing security, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and Zero Trust implementation are among the most in-demand skills among IT security teams worldwide. These skills are essential for addressing modern security challenges and protecting against advanced threats.
Is cybersecurity a good career?
Yes, cybersecurity is a highly rewarding career with strong job growth prospects, competitive salaries, and opportunities for advancement. The increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber threats ensure that skilled cybersecurity professionals will continue to be in high demand.
Is cybersecurity good for beginners?
Cybersecurity can be a great field for beginners, especially those with a strong interest in technology and problem-solving. There are many entry-level roles and resources available to help newcomers build foundational skills and advance their careers.
Is cybersecurity hard to study?
Studying or even just learning cybersecurity can pose challenges due to the rapidly evolving nature of threats and technologies, leading to swiftly outdated content. However, with dedication, practical experience, and a commitment to continuous learning, many find it a manageable and rewarding field to master.