Key Takeaways
- To become a data manager, you need to earn a relevant degree, gain hands-on experience, and obtain certifications.
- Success in this role requires a mix of technical skills like SQL and database management, along with soft skills related to leadership.
- Data management offers strong job prospects and competitive salaries, with demand across various industries.
In recent years, more than ever, companies and businesses rely on data to make smart decisions. However, for the insights gained and decisions made to be reliable and proper, the data used must be accurate, clean, and consistent. These are among the things that the data manager takes care of.
It’s a role worth looking into. But how to become a data manager? What path should you follow, which skills should you build, and most importantly, what do you stand to gain from this profession? You’ll find the answers here.
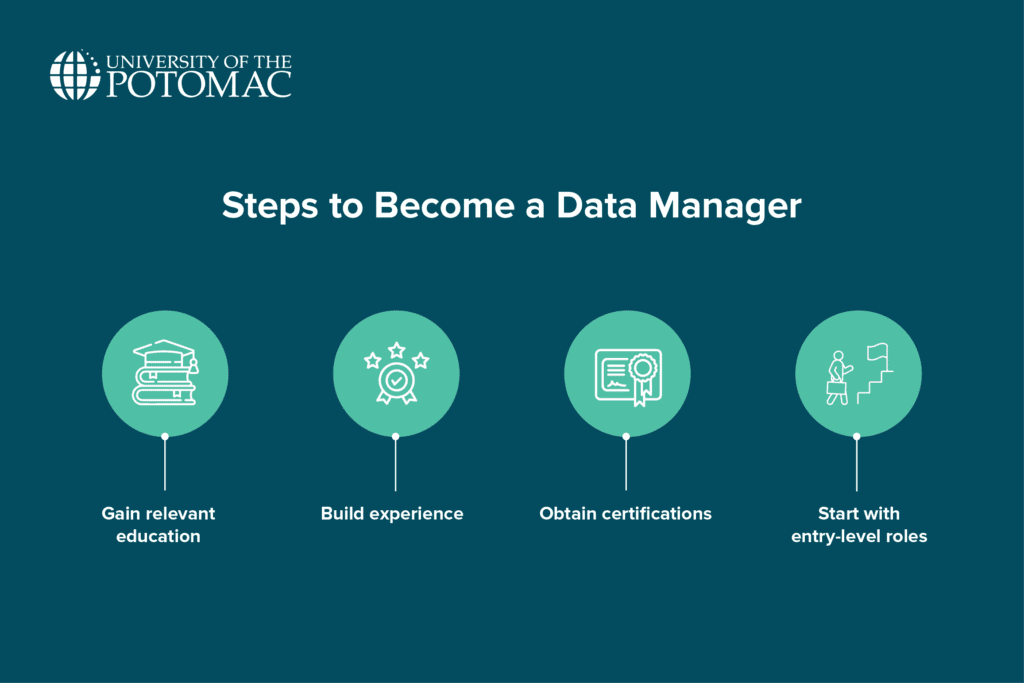
Steps to Become a Data Manager
In order to successfully pursue a career in data management, one needs more than mere curiosity in this field. The role requires dedication to formal education, a willingness to get hands-on with real-world data, and the commitment to continue learning even after you land your first job.
Becoming a data manager means combining theory with practice, structure with adaptability, and keeping a constant eye on accuracy and usability.
Gain relevant education
Education is the first step and the foundation for becoming a data manager. One of the most direct and simultaneously versatile paths you can choose at this stage is earning a degree in computer science.
A computer science degree introduces you to the core areas of data management but also gives you a strong foundation in related topics like databases, algorithms, system design, programming, and security—skills you can build on later, depending on your interests.
At the University of the Potomac, we offer a Computer Science BA program designed to give students a solid introduction to the field, with exposure to data structures, database management systems, and software development, among other areas.
Such a program will prepare you for a career in data management and a wide range of other roles beyond it, like software engineering, game design, cybersecurity, and mobile app development.
Other degree options that can also lead into the world of data management include Information Systems, Data Analytics, Business Intelligence, and Information Technology. All of them can provide the theoretical and practical foundation required to comprehend the collection, storage, and utilization of data in actual business settings.
At the University of the Potomac, we also offer a Master of Science in Data Analytics, a program that prepares individuals to use different statistical and quantitative methods, computational tools, as well as predictive models to help businesses, nonprofits, and government agencies with forecasting, risk assessment, and decision-making.
Though its primary focus is on analytics, many of the skills taught—such as working with data systems and applying data-driven strategies—are directly relevant to managing data in professional environments.
Build experience
Practical experience helps sharpen your abilities and build familiarity with the tools and platforms used in data management.
Such experience can come from many places. Internships, for example, are a common way to gain structured, supervised experience even if you are still in school. Freelance projects and open-source contributions can be some other great choices, as they enable you to practice your skills while building a portfolio.
You could also volunteer for data-related tasks in nonprofit organizations, join research projects, or participate in data hackathons and competitions. These all give you a chance to work with database management systems, experiment with different tools, and learn data security protocols—skills you’ll be expected to use every day once you step into the role of data manager.
Obtain certifications
Certifications can be an excellent way to help validate your skills and improve your credibility. They give employers confidence that you’re prepared for the demands of the role—especially if you’re transitioning into data management from a different field.
Some well-recognized certifications that can help boost your profile include:
- Certified Data Management Professional (CDMP)
- Google Data Analytics Certification
- AWS Certified Data Analytics
- Certified Information Management Professional (CIMP)
- Certified Analytics Professional (CAP)
Start with entry-level data roles
Before taking on a leadership role, entry-level positions offer you the opportunity to learn the ins and outs of data work. This step aims to give you an understanding of the processes involved in data collection, handling, reporting, compliance, and everything in between, rather than just helping you gain experience.
Some common roles you can begin with include:
- Data Analyst
- Database Administrator
- Business Intelligence Analyst
- Research Assistant
- Data Coordinator
Skills Required to Become a Data Manager
Becoming a data manager requires both technical and soft skills.
Technical skills
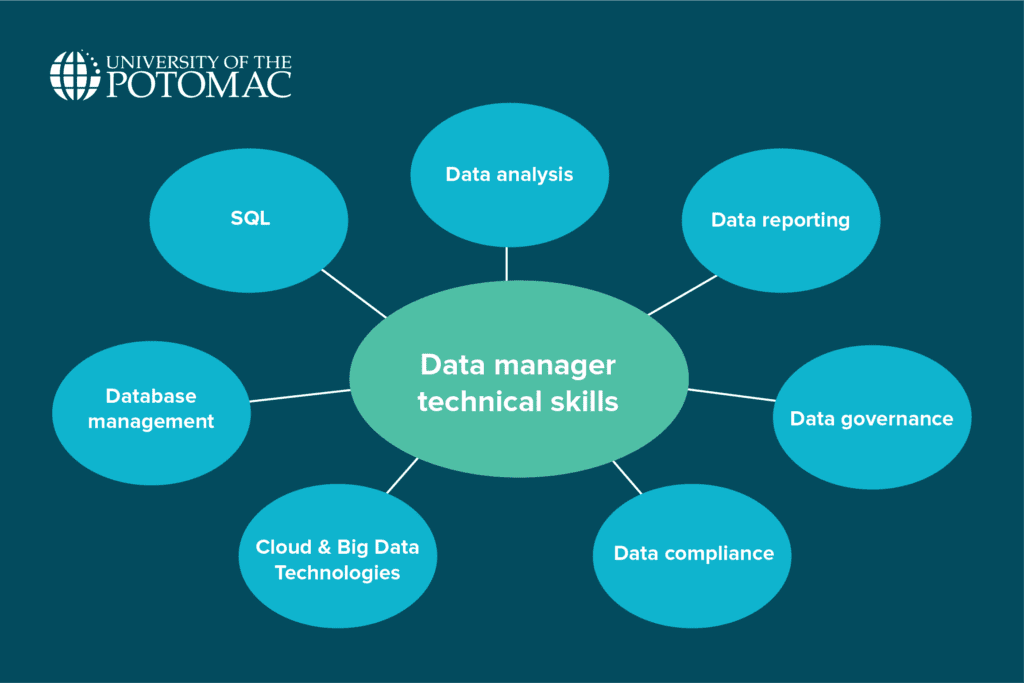
Data managers should know how to:
- Structure, maintain, and optimize databases
- Write SQL queries
- Analyze data to identify trends and insights
- Create reports that support business decisions
- Ensure data quality, integrity, and accessibility
- Follow privacy laws and industry regulations
- Work with cloud platforms and big data tools like AWS, Azure, or Hadoop
Soft skills
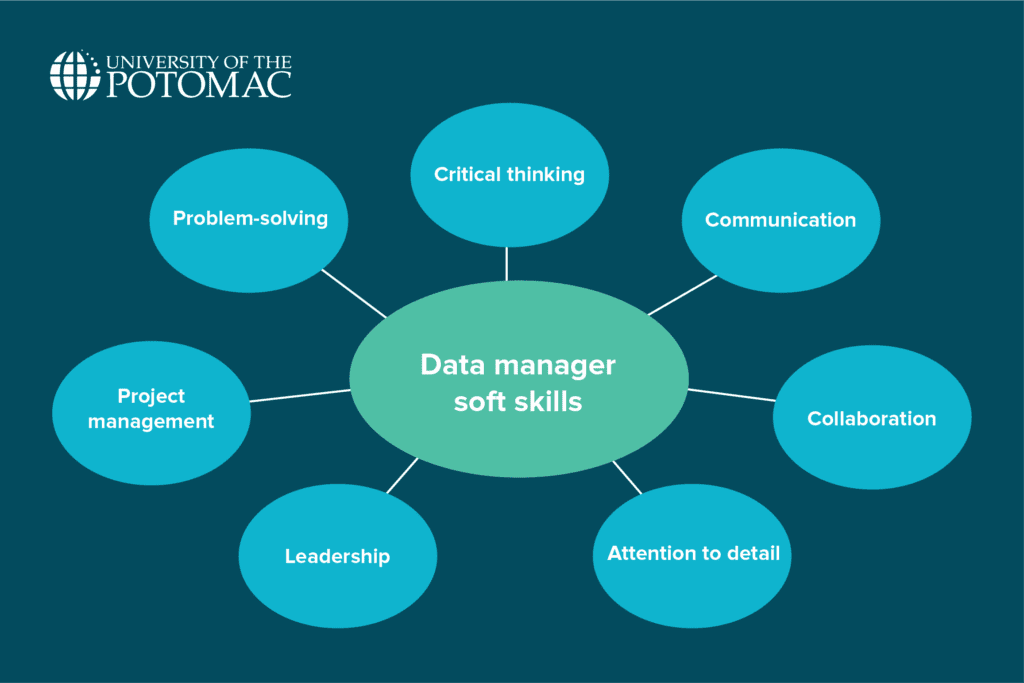
To be successful in a leadership role, professionals in data management should be skilled in:
- Finding solutions when data issues arise
- Critical thinking
- Explaining data processes and insights clearly to both technical and non-technical teams
- Working with others across departments
- Spotting inconsistencies or errors in large datasets
- Guiding teams and managing the direction of data-related initiatives
- Planning, executing, and overseeing data projects
Benefits of Becoming a Data Manager
With data now considered one of the most valuable assets in business, the role of a data manager has become more important—and rewarding—than ever. The financial stability you can have and the strong job market, in general, are among the most important benefits of working in data management.
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. We will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours.
If there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:
- We value your privacy.
Job outlook
Data management is a rapidly growing field. This growth can be attributed to the many digital transformations that have happened in recent years, the rise of artificial intelligence, as well as the explosion of big data.
Data storage, security, and interpretation have become essential components of any business as organizations continue to gather data. Industries like finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and tech are just a few of the many that rely heavily on data management to ensure accuracy, maintain security, and support real-time decision-making. With all of this, data managers are crucial in every way.
To be more precise, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment of computer and information systems managers—which includes data managers as well—is projected to grow 17% from 2023 to 2033.
Salary expectations
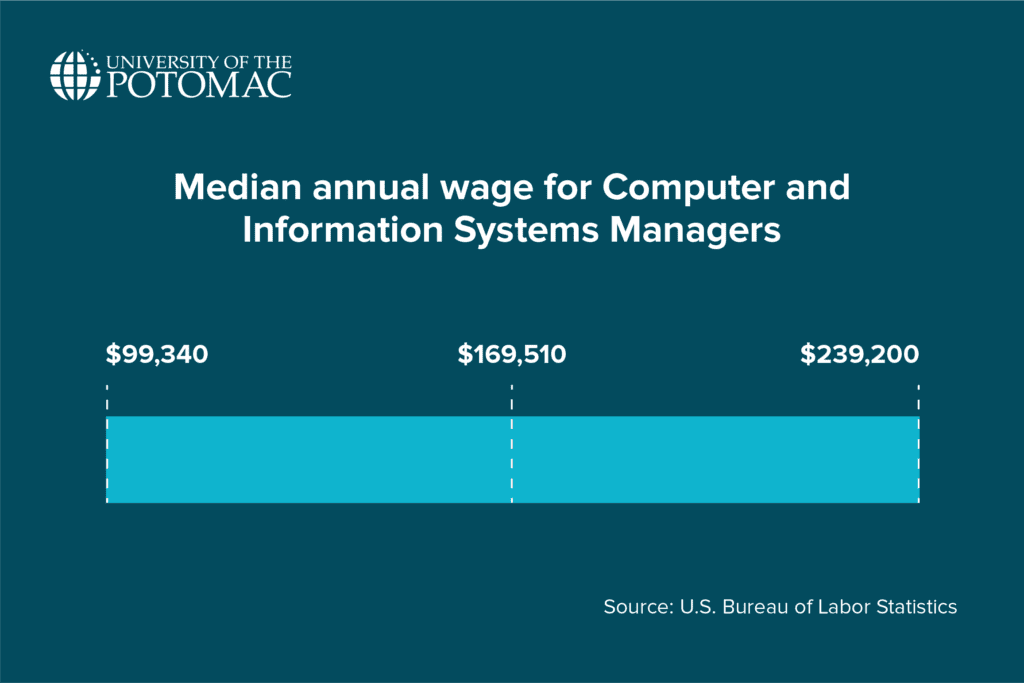
Naturally, high demand for a job tends to translate into high salaries. That’s because organizations compete for skilled professionals who can handle their growing data needs, which drives up compensation.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that the median annual wage for computer and information systems managers was $169,510 in 2023.
Although pay varies by industry, location, and experience, even the lowest 10% of workers in the field made about $99,340 annually, while the top 10% made up to $239,200.
Is a Career as a Data Manager the Right Path for You?
If you’re trying to figure out whether data management is the right fit, the best thing to do is start by asking yourself these two important questions:
- Do you see yourself having a career that is centered around data?
- Are you comfortable using technology and learning new tools like databases, spreadsheets, or data visualization software?
But it’s not just about the data—you’ll also need to enjoy structure, organization, and leading projects or teams. If you’re someone who can balance technical thinking with managing tasks, timelines, and communication across departments, that combination will serve you well in this role.
It also helps if you’re motivated by problem-solving. Data managers are often the ones who find errors, or even if they’re not the ones finding them, they’re the ones people go to once they do. So, if you’re someone who values clear, impactful work that supports decisions across a whole organization, this role offers just that.
Lastly, you should always consider your long-term goals. Consider your goals for both your personal and professional life and whether data management can help you achieve them.
Start Your Journey as a Data Manager
Data management is a career option with strong growth, great salaries, and relevance across many industries. With commitment to your education, hands-on experience, and the right certifications, success is absolutely achievable.
As you continue to build your skills and gain experience, you’ll find opportunities to grow, specialize, and take on greater responsibility in the field. All it takes is a solid foundation and the drive to keep learning.
And when it comes to laying that foundation, the University of the Potomac is the best place to start.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a data manager and a data analyst?
A data analyst focuses on numbers in order to find patterns and insights. Whereas the data manager is the one making sure all that data is clean, secure, and exactly where it needs to be before anyone else, including the analyst, can use it.
Do data managers need to know coding?
In most cases, yes—at least the basics. Knowing how to write SQL queries or use languages like Python or R can make a big difference when you’re working with large datasets or setting up systems.