Embarking on your college journey is an exciting and transformative experience filled with new opportunities, challenges, and adventures. At the heart of this adventure lies a concept that is both your guiding star and a crucial puzzle piece: credit hours. Now, you might wonder, “What are these credit hours?” Buckle up because understanding credit hours is like discovering the hidden map to your academic success and personal growth.
Understanding Credit Hours
Credit hours represent the numeric academic value assigned to a particular course. They provide a means to assess the relative difficulty and time commitment associated with different classes.
Typically, one credit hour equates to one hour of traditional class instruction per week over a semester. However, this measure goes beyond classroom hours and considers the additional time required for readings, assignments such as research papers, and studying.
For instance, a standard three-credit-hour course generally demands three hours of weekly in-class attendance, complemented by extra hours of independent study. In essence, credit hours reflect the academic workload and depth of learning expected from a course.
Contact Hours
Contact hours are a critical element within the realm of credit hours. They represent the hours students spend in direct contact with instructors through lectures, discussions, or laboratory sessions. These hours are valuable for acquiring knowledge, seeking clarification, engaging in discussions, and receiving guidance.
Contact hours vary among courses and disciplines: some may include extensive in-person meetings, while others rely more on independent study.
Understanding the relationship between contact hours and credit hours is crucial because it directly affects your engagement with the course material, your ability to ask questions, and the overall quality of your learning experience.
How Many Credit Hours Do I Need To Graduate College?
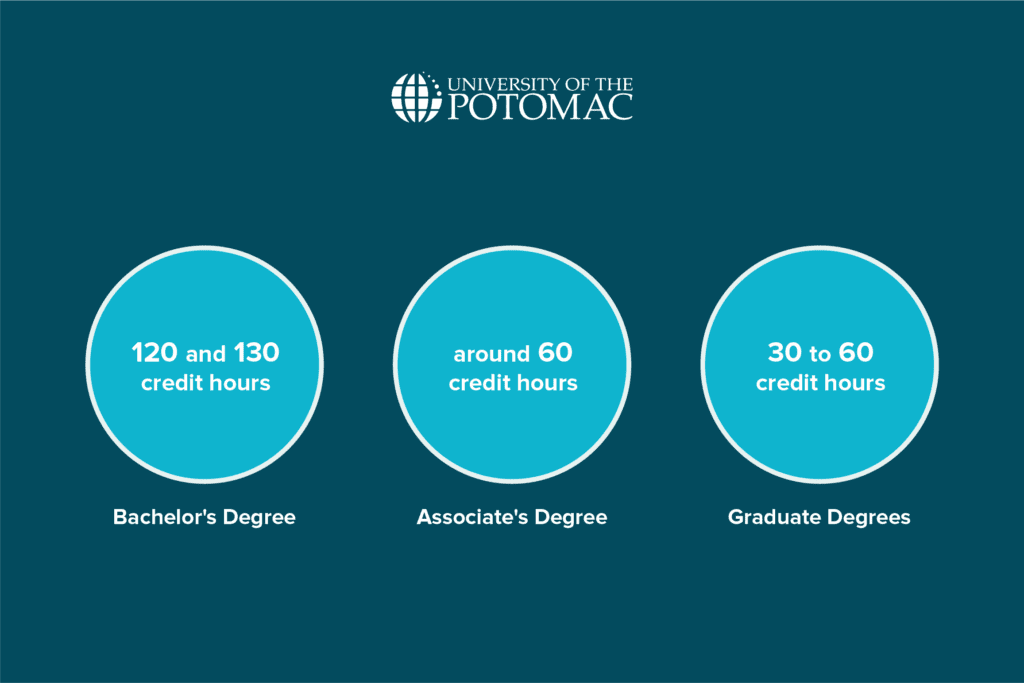
The number of credit hours required to graduate from college can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the specific college or university you attend, your chosen major or degree program, and any additional requirements or electives you decide to pursue. However, there are some general guidelines you can consider:
- Bachelor’s Degrees: A typical Bachelor’s degree program usually requires between 120 and 130 credit hours in the United States. This translates to approximately four years of full-time study, assuming you take the standard course load of 15 credit hours per semester.
Certain programs may require a higher or lower number of credits, so it’s essential to consult your college’s catalog or academic advisor for precise information.
- Associate’s Degrees: Associate’s degree programs commonly require about 60 credit hours, typically achievable in two years of full-time study. Community colleges often offer associate programs to provide a foundational education or prepare students for specific careers.
- Graduate Degrees: The credit hour requirements for graduate degrees (Master’s and Doctoral degrees) can vary widely based on the field of study, program, and institution.
Master’s programs generally require 30 to 60 credit hours, while Doctoral programs may require 60 or more. Additionally, research and dissertation credits may be part of graduate degree requirements.
Credit Hours vs. Course Load
Credit hours represent the academic value of a specific course, indicating the time and effort it demands. You can also think of them as the currency of your education – the more credit hours you accumulate, the closer you are to graduation.
On the other hand, the course load refers to the number of courses you enroll in during a given semester. While credit hours provide insight into the depth and intensity of each class, your course load determines the overall weight of your academic commitments.
Differentiating Credit Hours from the Number of Courses
It’s easy to confuse credit hours with the number of courses you take. Still, they represent distinct aspects of your college education. As mentioned, credit hours measure the time commitment and depth of each course. In contrast, the number of courses, also known as your course load, counts how many classes you’re enrolled in.
For example, a three-credit-hour course may require as much time and effort as a four-credit-hour course, even though you’re taking one fewer course in the former case. Understanding this difference is essential because it allows you to tailor your academic schedule to your strengths, weaknesses, and interests.
You might opt for a lighter course load with more challenging, credit-intensive classes or a heavier course load with a mix of lighter and heavier credit-hour courses. This flexibility empowers you to customize your college experience to align with your goals and priorities, ensuring a fulfilling and successful journey. Balancing these two factors is crucial in managing your college experience effectively.
Balancing Credit Hours for a Manageable Workload
Finding the right balance of credit hours for a manageable workload is an art every college student must master. A standard full-time workload is typically 12-15 credit hours per semester. However, this can vary based on your academic goals, personal circumstances, and the difficulty of your courses.
When deciding on your course load, consider your major’s requirements, your part-time job, extracurricular activities, and any personal commitments. Overloading credit hours may lead to burnout and impact your academic performance while underloading could delay your graduation. Striking the right balance ensures steady progress toward your degree while maintaining a healthy balance.
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. We will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours.
If there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:
- We value your privacy.
It’s important to remember that quality often trumps quantity regarding credit hours. Instead of focusing solely on accumulating credits, prioritize the depth of your learning experience. Engage actively in your courses, seek out opportunities for research or internships, and explore subjects that genuinely interest you. By doing so, you will graduate with the required credit hours and a rich and meaningful college experience that prepares you for the future.
Transferring Credits
Transferring credits is a valuable option for college students, offering the opportunity to make the most of your academic journey. Whether changing schools, pursuing a new major, or simply looking to broaden your horizons, understanding the intricacies of credit transfer can save you time and money.
To begin, research your current institution’s transfer policies and requirements, as they can vary widely. Identify the courses you intend to transfer and make sure that they align with your new academic goals.
Additionally, maintain clear communication with academic advisors at your current and prospective institutions to ensure a smooth transition. Transferring credits streamlines your educational path and allows you to leverage your prior knowledge and experience, making your college journey a more flexible and tailored experience.
So, if you’re considering a change, explore credit transfer opportunities to unlock the full potential of your higher education.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding credit hours, course loads, and the process of transferring credits are essential skills for any college student. They empower you to navigate the academic maze effectively and maximize your educational adventure. Finding the right balance between credit hours and course loads can create a manageable workload that promotes both success and well-being. And, when it comes to transferring credits, remember that it’s not just about changing schools; it’s about customizing your educational journey to align with your aspirations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
What are credit hours in college, and why are they important?
Credit hours quantify the time and effort required for a course. They’re vital because they determine your workload, graduation progress, and your eligibility for financial aid.
How are credit hours assigned to different courses?
Credit hours are assigned based on the course’s instructional time, including class hours, lab work, and expected study time. Typically, one credit hour represents one hour of in-class instruction per week and extra appropriate outside preparation.
What is the difference between credit hours and the number of courses I take?
Credit hours measure the depth of individual courses, while the number of courses determines your overall course load. You can adjust both to manage your workload.
What are contact hours?
Contact hours are the time spent directly interacting with instructors, like lectures or labs. They are a subset of credit hours and crucial for active learning.
How do credit hours affect my workload and schedule?
Credit hours influence your workload by indicating the time you’ll spend on a course. Balancing them in your schedule is essential to manage your academic life effectively.
Can I adjust the number of credit hours I take each semester?
Yes, you can adjust your course load by adding or dropping courses. Be mindful of credit hour requirements for your degree.
Is there a maximum limit to the number of credit hours I can take in one semester?
Colleges often set a maximum credit hour limit per semester. Numbers vary but typically range from 18 to 20 credits.
How can I plan my course schedule to graduate on time with the right number of credit hours?
Consult with your academic advisor, create a degree plan, and ensure you meet your major and general education credit hour requirements.
Can I transfer credit hours between colleges?
Yes, you can transfer credit hours, but policies vary among institutions. Work closely with advisors and follow transfer guidelines to ensure a smooth transition.










