For those aspiring to enter the accounting field, the abbreviation CPA is likely one they have encountered, signaling a crucial milestone: the CPA exam. This exam is a must for individuals in various accounting roles, establishing a benchmark of competence and expertise. Understanding the CPA exam’s structure and scoring methodology is key to successful preparation.
In this article, we will delve into the essential details of this exam, answering some important questions such as “What is the CPA exam pass rate?” and “How is the CPA exam scored?” So, keep reading to explore these critical aspects and enhance your readiness for the exam.
What Is the CPA Exam?
The Certified Public Accountant (CPA) exam is a rigorous assessment designed to ensure that candidates possess the necessary knowledge and skills to achieve CPA licensure. This credential unlocks a multitude of career opportunities in accounting and finance.
Administered by the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA), the CPA exam is recognized as one of the most challenging professional exams, requiring thorough preparation and a deep understanding of various accounting principles and practices.
The exam is divided into four sections, each covering a different area of accounting and business knowledge:
- Auditing and Attestation (AUD): This section evaluates a candidate’s understanding of the auditing process, including the principles and procedures involved in auditing financial statements. It also covers attestation engagements, preparation, compilation, and review engagements, as well as ethics related to audit engagements.
- Financial Accounting and Reporting (FAR): This section assesses a candidate’s knowledge of financial accounting standards and reporting requirements for business enterprises, not-for-profit organizations, and government entities. It covers various topics, including financial statement preparation, GAAP principles, and accounting for multiple types of transactions and events.
- Regulation (REG): The REG section focuses on taxation, ethics, and business law. It includes federal taxation of individuals, entities, and property transactions, as well as professional responsibilities and legal obligations of CPAs.
- Three options for the specialized section that include:
- Business Analysis and Reporting (BAR): This CPA section focuses on evaluating and reporting financial information within organizations. It covers financial statement analysis, managerial accounting, forecasting and budgeting, performance management, and decision-making processes based on financial data. BAR prepares candidates to interpret financial statements, analyze business operations, and provide insights to stakeholders for effective decision-making.
- Information Systems and Controls (ISC): ISC emphasizes integrating technology with accounting practices. It includes topics such as IT governance, information systems auditing, data management and analytics, cybersecurity, and internal controls related to information systems. This section equips candidates with the knowledge needed to assess and manage risks associated with information technology in accounting and business environments.
- Tax Compliance and Planning (TCP): TCP covers federal taxation laws and regulations, focusing on compliance with tax laws and strategic tax planning. Topics include individual and entity taxation, tax research methods, tax implications of business transactions, tax compliance issues, and tax policy considerations. Candidates learn to navigate complex tax codes, advise clients on tax matters, and optimize tax strategies for individuals and businesses.
Each section is designed to test a candidate’s ability to apply accounting knowledge in practical, real-world scenarios. The exam format includes multiple-choice questions, task-based simulations, and written communication tasks, providing a thorough assessment of a candidate’s competency in accounting and related fields.
How much time does the exam require?
Preparing for and taking the CPA exam requires a significant time commitment. Candidates must study for each section of the exam and manage their time effectively to ensure they are well-prepared for the exam day. On average, candidates spend between 300 and 400 hours studying for the entire exam, translating to approximately 80 to 100 hours per section.
The time required to prepare for each section can vary based on a candidate’s background and familiarity with the material. For instance, candidates with a strong financial accounting background might need less time to prepare for the FAR section, while those less familiar with business law might need to allocate more time to the REG section.
In addition to study time, candidates must also consider the time required to schedule and take the exam. The CPA exam is offered during specific testing windows throughout the year, and candidates must schedule their exams within these windows. Each section of the exam is four hours long, equaling 16 hours in total, and candidates can take the sections in any order they choose. However, they must pass all four sections within an 18-month rolling period to qualify for licensure.
How Is the CPA Exam Scored?
The CPA exam uses a scoring system ranging from 0 to 99, with a passing score of 75 required for each section. AICPA uses a scaled scoring system to ensure consistency and fairness in the exam results. This system accounts for the difficulty level of each exam version, ensuring that all candidates are held to the same standard regardless of which version of the exam they take. Consequently, a score of 75 represents the same level of proficiency across all exam versions.
Multiple-choice questions
Multiple-choice questions (MCQs) make up a significant portion of each section of the CPA exam. Each section includes a mix of pre-tested and operational MCQs. The pre-tested questions do not count toward the final score, while the operational questions are scored based on their difficulty level. More difficult questions are worth more points.
Task-based simulations
Task-based simulations (TBSs) are another critical component of the CPA exam. These simulations present candidates with real-world scenarios requiring them to apply their accounting knowledge to solve problems. TBSs are scored based on the accuracy and completeness of the candidate’s responses.
Written communication tasks
The section of the CPA exam that is focused on Business Environment and Concepts (BEC) includes written communication tasks, which assess a candidate’s ability to write clearly and effectively in a professional context. These tasks are scored based on the quality of the writing, including organization, clarity, and relevance to the given topic.
CPA Exam Pass Rates: Breaking Down Each Section
The CPA exam pass rates are published by AICPA on a quarterly basis. It is important to understand that these rates reflect the performance of candidates against an established standard of competence. Therefore, fluctuations in pass rates typically indicate changes in candidate preparedness rather than changes in exam difficulty.
For the first quarter of 2024, the CPA exam pass rates for each section were as follows:
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. We will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours.
If there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:
- We value your privacy.
- Auditing and Attestation (AUD): 44.63%;
- Financial Accounting and Reporting (FAR): 41.92%;
- Regulation (REG): 63.42%;
- Business Analysis and Reporting (BAR): 42.94%;
- Information Systems and Controls (ISC): 50.93%;
- Tax Compliance and Planning (TCP): 82.36%.
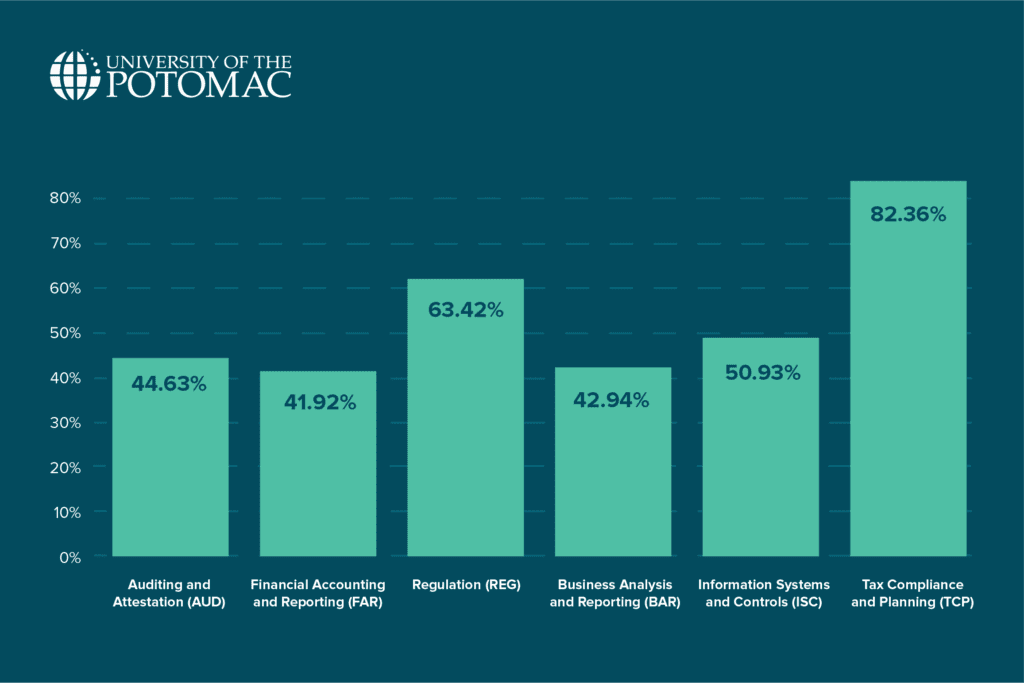
These rates provide an early indication of candidate performance for the year. Notably, the TCP section had the highest pass rate at 82.36%, while FAR was the most challenging, with a pass rate of just 41.92%.
Looking back at the calendar year 2023, the cumulative pass rates for each section were:
- Auditing and Attestation (AUD): 46.92%;
- Business Environment and Concepts (BEC): 56.52%;
- Financial Accounting and Reporting (FAR): 42.94%;
- Regulation (REG): 59.19%.
These rates were broken down quarterly, showing how candidates’ performance varied throughout the year. For instance, the BEC section saw a significant drop in pass rates in the fourth quarter, down to 38.17%, compared to higher rates earlier in the year. This kind of fluctuation can be attributed to various factors, including the time of year and changes in candidate preparation levels.
The pass rates offer several insights. Firstly, despite periodic fluctuations, the overall consistency in pass rates across different quarters indicates that the CPA exam maintains a stable level of difficulty. Additionally, the higher pass rates generally suggest better preparation among candidates. For example, the consistently high pass rate for the TCP section indicates that candidates are particularly well-prepared for this section. Lastly, sections like FAR and AUD consistently have lower pass rates, highlighting their demanding nature and the need for thorough preparation.
Tips for Passing the CPA Exam
Preparing for and passing the CPA exam requires a strategic approach, dedication, and effective study techniques. Here are some valuable tips for passing the CPA exam:
- Create a study schedule and stick to it, allocating ample time to cover all exam topics;
- Utilize high-quality review courses and study materials to reinforce your understanding of key concepts;
- Practice with multiple-choice questions (MCQs) and task-based simulations (TBSs) to familiarize yourself with the exam format;
- Take advantage of practice exams to assess your knowledge and identify areas that need improvement;
- Focus on your weak areas, but also regularly review your strengths to maintain a balanced knowledge base;
- Stay disciplined and avoid procrastination by setting specific study goals and deadlines;
- Join study groups or find a study partner to stay motivated and gain different perspectives on complex topics;
- Get enough sleep, exercise regularly, and take breaks when needed to maintain your physical and mental health;
- Stay positive and confident in your abilities, remembering that consistent effort and preparation will pay off.
Conclusion
The CPA exam is a challenging but essential step for aspiring CPAs. Understanding the exam’s structure, the time required for preparation, the scoring process, and the pass rates for each section can help candidates develop effective study strategies and increase their chances of success.
With dedication, thorough preparation, and a well-structured study plan, candidates can achieve their goal of becoming a certified public accountant and unlock a wealth of career opportunities in the accounting profession.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does CPA mean?
CPA, an acronym for Certified Public Accountant, is a professional designation given to qualified accountants who pass the CPA exam and meet additional state certification and experience requirements.
What is the difference between a CFA and a CPA?
A CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst) focuses on investment management, portfolio management, and financial analysis, while a CPA (Certified Public Accountant) specializes in accounting, auditing, tax, and regulatory compliance.
How much does the CPA exam cost?
The cost of the CPA exam varies by state but typically amounts to around $1,000, including application fees, examination fees, and registration fees for each section.