Key Takeaways
- Leadership has long been a fundamental part of society, influencing everything from households and communities to corporations and governments.
- A leadership style is the approach a leader takes to guide, motivate, and manage a team.
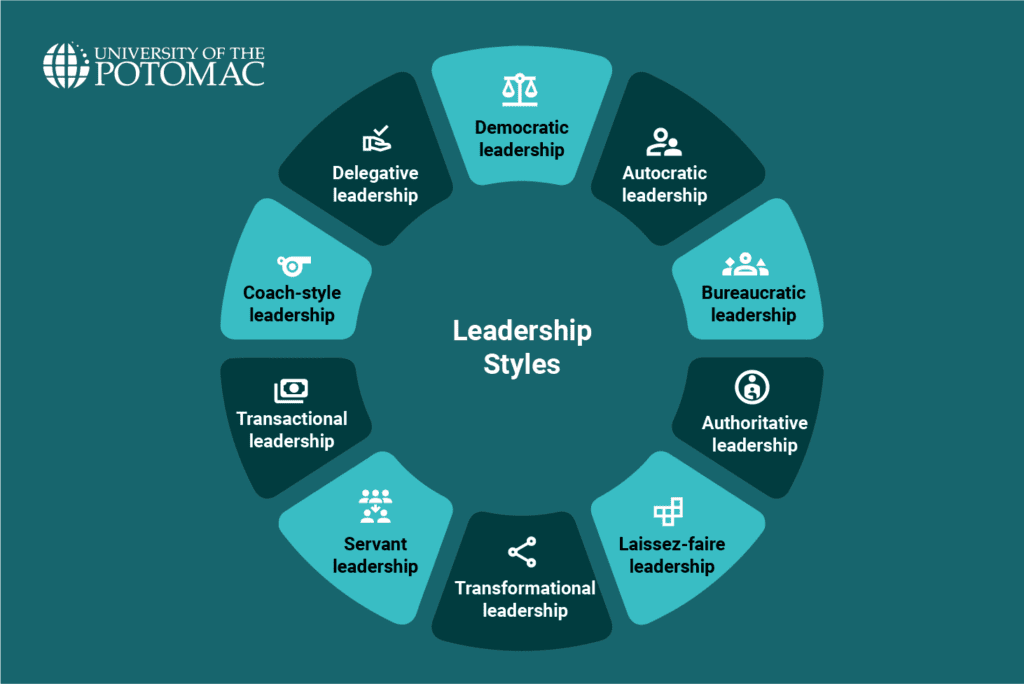
- There are many leadership styles, including democratic, autocratic, transformational, laissez-faire, and servant leadership.
- The effectiveness of a leadership style depends on the leader’s abilities, team structure, and the specific demands of a situation.
Leadership takes many forms and reaches into every aspect of society—from those guiding families and small communities to elected officials in governments and authoritarian rulers who exercise full control over their people. Leadership in itself is about making decisions and influencing others, but not all those that are leaders go about it the same exact way. Some inspire with a clear vision and motivate through collaboration, while others rely more on authority and control.
These varying approaches form what we recognize as different leadership styles. By understanding these styles, we gain insight into what makes leadership effective and how it influences organizations, societies, and even entire nations.
Leadership Styles
For years, researchers have studied leadership in an attempt to determine what makes certain leaders more effective than others. Although no particular leadership style has been proven to be universally superior to the other ones, these studies have provided some valuable insights into how different approaches influence individuals, teams, and entire organizations.
The effectiveness of a leadership style generally depends on the people involved, the environment in which they function, and the goals they set.
Democratic leadership
Democratic leadership is all about collaboration and shared decision-making. Leaders who display this style are always seeking input from the rest of their team before making any final decisions. That’s because they value different perspectives.
For example, in a brainstorming session, a democratic leader wouldn’t simply dictate their own opinions on the strategy but would instead encourage employees to share their ideas, discuss the pros and cons of each suggestion, and then collectively decide the best course of action.
Autocratic leadership
Autocratic leadership stands in contrast to the democratic approach because it revolves around centralized control in decision-making. These kinds of leaders make decisions independently, with little to no input from others.
While it might sound too rigid, this approach can be highly effective in situations where quick, decisive action is needed—such as the military or during crisis management.
Bureaucratic leadership
Bureaucratic leadership is rooted in structure, rules, and clear guidelines. This style is most effective in industries where compliance and precision are essential, such as government agencies, healthcare, and finance.
Leaders following this approach are primarily concerned with making sure that procedures are followed to the letter in order to reduce the risk of errors and inconsistencies. While it may not always encourage innovation, it is crucial for maintaining order and consistency in highly regulated environments.
Authoritative leadership
Authoritative leadership is oftentimes misunderstood as being harsh or overly controlling, but when applied correctly, it can be incredibly powerful. Leaders who use this style set a clear vision and direction, motivating their teams to work toward a common goal.
Unlike autocratic leaders, authoritative leaders explain the “why” behind their decisions and that tends to inspire confidence and commitment.
Laissez-faire leadership
Leaders with a laissez-faire leadership style take a more hands-off approach and give employees the freedom to make their own decisions. They trust their teams to be self-sufficient, stepping in only when necessary.
This style works exceptionally well in creative industries as spaces where employees need some level of autonomy and innovation in order to succeed. However, the employees must be highly skilled and self-motivated to be effective.
Transformational leadership
Transformational leaders inspire and motivate their teams to seek progress and surpass expectations. They focus on long-term growth, pushing individuals to develop their skills and embrace change.
This leadership style is particularly effective in organizations that need to evolve and innovate. It works well in environments where vision and motivation are the key factors that drive success, such as entrepreneurship, education, and tech industries.
Servant leadership
Servant leadership flips the traditional power dynamic, focusing on the needs of employees rather than the leader’s authority. A servant leader prioritizes the well-being and development of their team, encouraging a positive and supportive work culture.
This approach is often encountered in nonprofit organizations or companies with strong ethical missions. By creating a culture of trust and empowerment, servant leaders build organizations where employees feel valued and motivated to contribute their best.
Transactional leadership
Transactional leadership operates on a system of rewards and consequences. Leaders who adopt this style establish clear expectations and offer incentives for meeting targets while implementing penalties for underperformance. This approach works well in structured environments where productivity and efficiency are the primary goals, such as sales teams or military organizations.
While this leadership style is effective in driving short-term results, it may not encourage long-term creativity or innovation.
Coach-style leadership
Coach-style leadership, much like a sports coach guiding athletes, focuses on individual development. The ones using this approach provide constant feedback, encouragement, and skill-building opportunities to help employees grow.
This style is commonly seen in organizations that invest in employee training and mentorship. For example, a manager who schedules regular one-on-one meetings with employees to discuss career goals and offer tailored advice is demonstrating coach-style leadership.
Delegative leadership
Delegative leadership is considered an extension of the laissez-faire style. Leaders using this style aim to assign responsibilities based on individual strengths and encourage autonomy. It is particularly effective in environments where team members are highly skilled and self-driven.
Though it can help build confidence and accountability, it also requires careful balance to ensure that employees remain engaged and aligned with organizational goals.
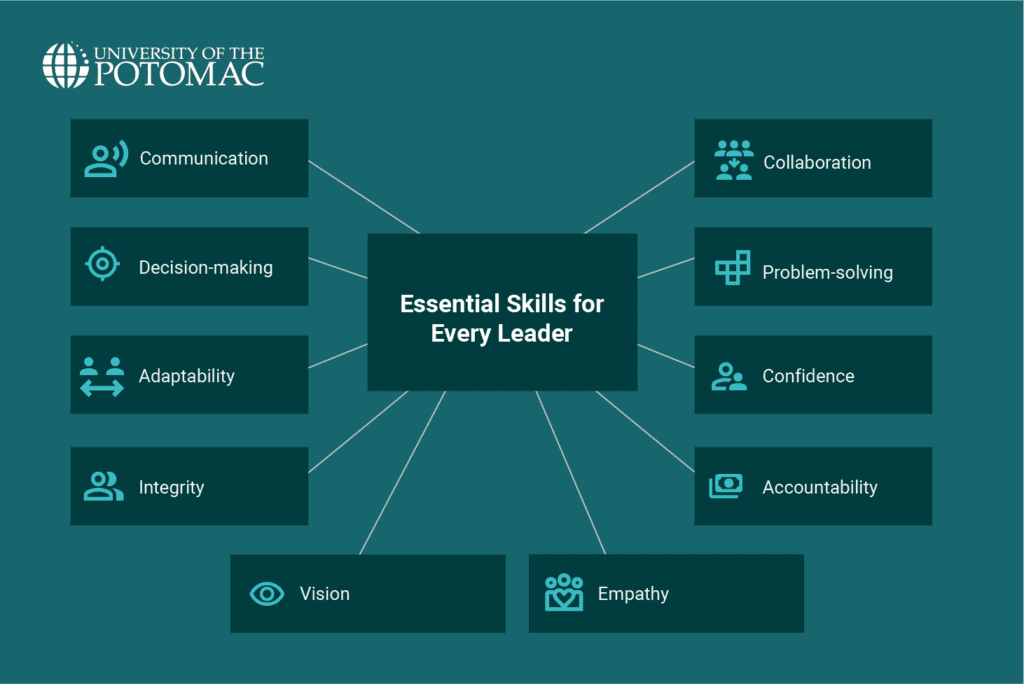
Essential Skills for Every Leader
Holding a leadership title does imply authority, but it doesn’t automatically make someone a leader. Leadership is about the ability to guide, inspire, and support others in achieving a common goal.
Regardless of their leadership style, there are certain core leadership skills that every great leader must develop. These skills include:
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. We will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours.
If there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:
- We value your privacy.
- Communication: Clearly conveying ideas, setting expectations, managing conflicts, and ensuring team alignment to prevent confusion and misinterpretation.
- Decision-making: Evaluating information, considering options, and making well-informed choices that balance intuition with data-driven insights.
- Adaptability: Responding to change with flexibility, embracing innovation, and guiding teams through transitions while maintaining momentum.
- Integrity: Earning trust through honesty, fairness, and leading by example while fostering a culture of ethical responsibility.
- Vision: Thinking beyond immediate challenges, setting a compelling direction, and keeping teams motivated and focused on long-term goals.
- Empathy: Actively listening, recognizing different perspectives, and providing support to create a collaborative and inclusive work environment.
- Accountability: Owning decisions, learning from mistakes, and ensuring that both leaders and team members take responsibility for their contributions.
- Confidence: Displaying confidence in decisions while remaining open to constructive feedback and continuous learning.
- Problem-solving: Identifying root causes of challenges, analyzing potential solutions, and implementing strategies with resilience and creativity.
- Collaboration: Encouraging teamwork, valuing diverse input, and fostering an environment where every contribution is recognized and appreciated.
How to Identify Your Leadership Style
Some people naturally gravitate toward a particular leadership style, shaped by their personality, past experiences, and even how they interacted in friend groups or worked on school projects.
Maybe you were always the one taking charge, or perhaps you preferred guiding from the sidelines while ensuring everyone was heard. Others may not have such a clear sense of their leadership identity or might simply be wondering if a different approach would make them more effective.
If you’re unsure where you stand or want to refine your leadership skills, here are a few steps to help you identify your leadership style:
Reflect on past experiences and feedback
Think back to times when you found yourself in a leadership position—whether in school, at work, or even in informal settings like group projects or volunteer activities. Did you naturally take charge, or did you prefer to support and guide others behind the scenes?
Consider the feedback you’ve received from colleagues, friends, or mentors—have they pointed out specific strengths or tendencies in your leadership approach? Recognizing patterns in how you lead and how others perceive your leadership can provide valuable insights into your style.
Take leadership style assessments
There are various online tools, quizzes, and personality tests that analyze leadership behaviors and decision-making tendencies. They can provide valuable insights into which style might suit you best.
While these tests aren’t definitive labels, they can help you better understand your strengths, blind spots, and areas where you may need improvement.
Experiment with different approaches
Remember that the leadership style also depends on the team, environment, and challenges at hand. So, try shifting your approach in different situations. Take a more authoritative role in one setting, then focus on collaboration in another.
Pay attention to how your team responds, what feels natural to you, and which methods yield the best results. By exploring different leadership techniques, you’ll develop a more well-rounded approach.
Recognize the importance of adaptability.
No matter what leadership style you naturally lean toward, flexibility is still important. Strong leaders don’t stick to just one way of doing things—they adjust their leadership style based on their team’s needs, the goals at hand, and external circumstances.
The Bottom Line
Leadership has always been a part of society, from influencing communities to steering businesses toward growth and innovation. In the corporate world, leadership and management go hand in hand.
So, if you’re considering a career in business and aspire to lead a team or even run a company one day, Potomac’s Bachelor of Science in Business provides the perfect foundation, equipping you with the skills and knowledge needed to step confidently into a leadership role.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the most effective leadership style?
There’s no universally “most effective” leadership style—it depends on the team, organization, and situation.
What’s the best leadership style?
The best leadership style is the one that aligns with your strengths while promoting a positive and productive environment. A strong leader knows when to be authoritative, when to collaborate, and when to empower others.