“Level of education” refers to the different stages of formal education available to individuals. Continue reading to understand the formal educational journey from preschool to postsecondary education.
Education is the cornerstone of personal and societal growth and is often referred to as the foundation of a society. And rightfully so! The education system consists of major levels of education, each developing certain skills necessary for facing the complexities of life.
Therefore, understanding the various levels of education that make up the educational system can help you decide on the best option for achieving your personal and professional goals.
In this article, we’ll explore the major levels of education and their role in your life. We’ll also examine the importance of education levels on career opportunities and emerging trends in education. Let’s dive right in!
Understanding the Different Levels of Education
Levels of education refer to the different stages of formal education, each serving as a building block marking milestones in an individual’s academic and professional journey. Understanding each level that makes up an individual’s educational journey throughout their life helps them make informed decisions about their career path and further education.
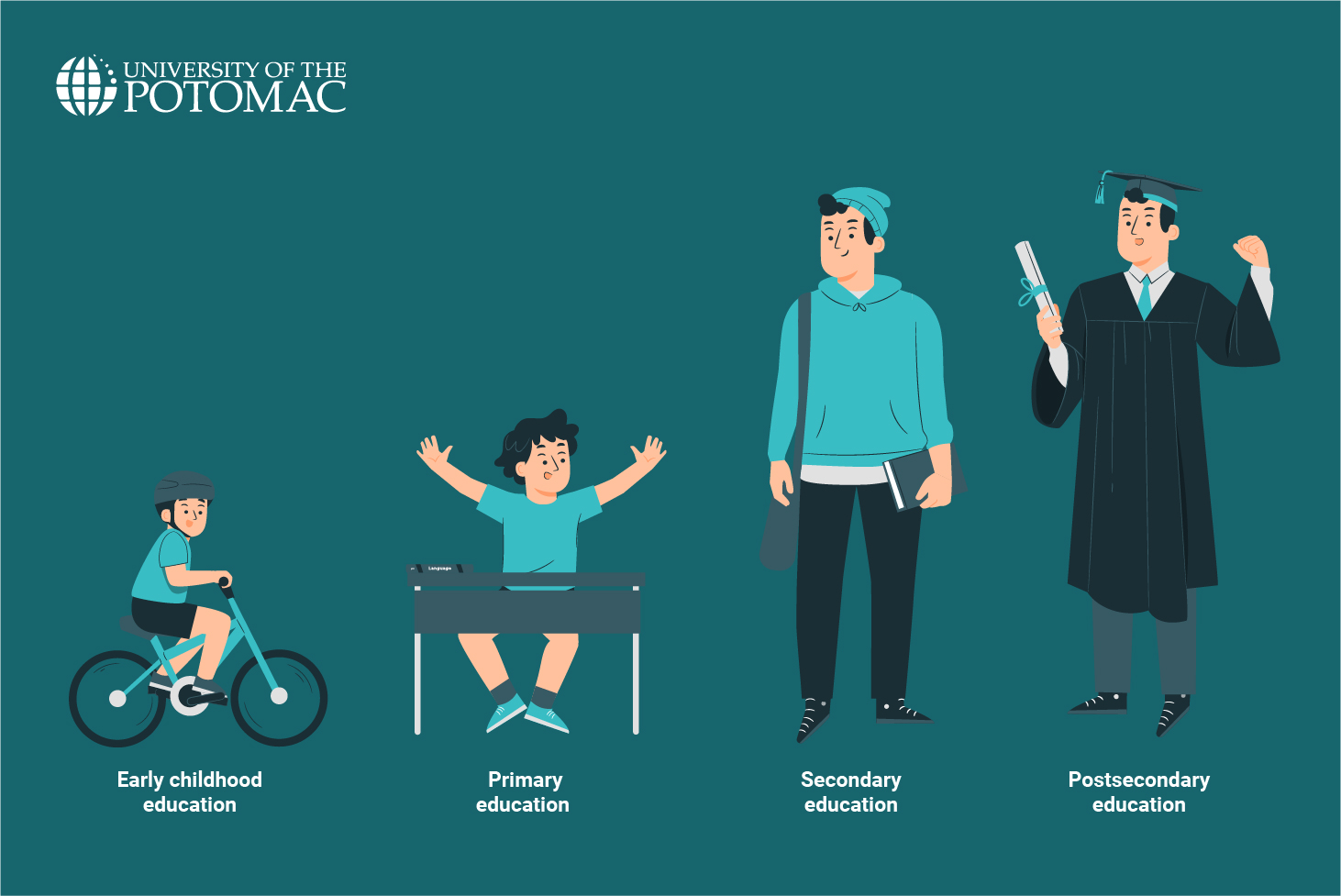
The education system is categorized into four major levels:
- Early childhood education
- Primary education
- Secondary education
- Postsecondary education
Let’s explore each level of education in detail.
The Major Levels of Education
The levels of education provide a learning structure that corresponds to the human developmental stages. Each equips students with the necessary knowledge and skills to proceed to the next level. Here are the major levels of education.
Early Childhood Education
Early childhood education plays a vital role in a child’s overall development and provides the foundation for future learning. It encompasses the initial years of a child’s life to the age of six. It focuses on establishing a solid cognitive, emotional, and social foundation, ensuring their readiness for formal schooling. Early childhood education encompasses preschool education and kindergarten.
Preschool Education
Preschool education is often the first educational experience for children. The age range at this level is usually three to five years.
Preschool education provides a nurturing environment that fosters curiosity, creativity, and problem-solving skills. Children engage in various activities that help develop their fine and gross motor skills. They also learn to interact with their classmates, take turns, and share.
Pre-elementary/Kindergarten
Pre-elementary or kindergarten education serves as a crucial transition between preschool and primary education. It focuses on building a strong foundation in literacy and numeracy skills as well as promoting emotional development and social interaction.
In kindergarten, children are introduced to early literacy skills, such as letter recognition, phonics, and basic reading comprehension. Common activities that promote language development include storytelling, rhyming, and vocabulary building.
Kindergarten also emphasizes the development of numeracy skills. Children learn to recognize numbers, count, and solve simple mathematical problems.
Primary or Elementary Education

Primary or elementary education lays the groundwork for further levels of education and is crucial in shaping a child’s character and values. It covers grades one through six, with children starting school at six years old and completing primary education by the time they’re 12.
During this period, children become familiar with various subjects that form the building blocks of their future learning. The curriculum’s width increases as students move up from one grade to the next, with core subjects being English language, arts, mathematics, science, and social studies. In addition to core subjects, children develop social skills and participate in sports and extracurricular activities.
Secondary Education
Children typically start secondary education after elementary school, which consists of grades seven to 12. Secondary education bridges the gap between elementary schooling and higher education and involves junior high school or middle school and high school.
Junior High School (Middle School)
Middle school starts with grade six and ends with grade eight. Students attending middle school are around age 12 to 14.
Core subjects in middle school include:
- English
- Mathematics
- Sciences
- Social studies
Students also become exposed to a broader range of subjects beyond the core curriculum. These subjects include literature, history, geography, and foreign languages, which broaden their knowledge and skills.
Middle school students often have the opportunity to choose elective courses, such as art, music, technology, and other specialized subjects, that allow them to explore their interests.
High School
High school is the final mandatory education and serves as the foundation for either entering the workforce or pursuing higher education. This stage includes grades nine through 12 for students ages 14 to 18.
The core curriculum in high school includes subjects like English, mathematics, science, and social studies. However, these subjects are more advanced and in-depth than those in middle school.
High school students can also choose from a broader range of elective courses, such as foreign languages, technology, and arts, allowing them to explore their interests and potential career paths. Furthermore, students can participate in various extracurricular activities that support student development in areas beyond academics, such as sports teams, clubs, music, and art programs.
Postsecondary Education
Postsecondary refers to the formal schooling received after high school. Common types of postsecondary education include college and vocational training.
Types of Postsecondary Institutions
Here are the most common types of postsecondary institutions.
- Community Colleges: These institutions offer two-year programs, associate degrees, and certifications.
- Vocational and Technical Schools: These postsecondary institutions offer skill-based training for specific careers, such as electrician, health technician, massage therapist, carpentry, and plumbing.
- Four-Year Colleges and Universities: These higher-education institutes offer programs from bachelor’s to doctoral degrees.
- Online and Hybrid Learning Programs: There’s been steady growth in e-learning programs as these programs offer flexibility, accessibility, and affordability.
Higher Education: Degrees and Certifications
Higher education refers to the postsecondary education following secondary education. It includes undergraduate (associate and bachelor’s degrees) and graduate (master’s and doctoral degrees) programs offered by colleges, universities, and other institutions of higher learning. Higher education provides advanced knowledge and skills, preparing students for professional careers and advanced degrees.
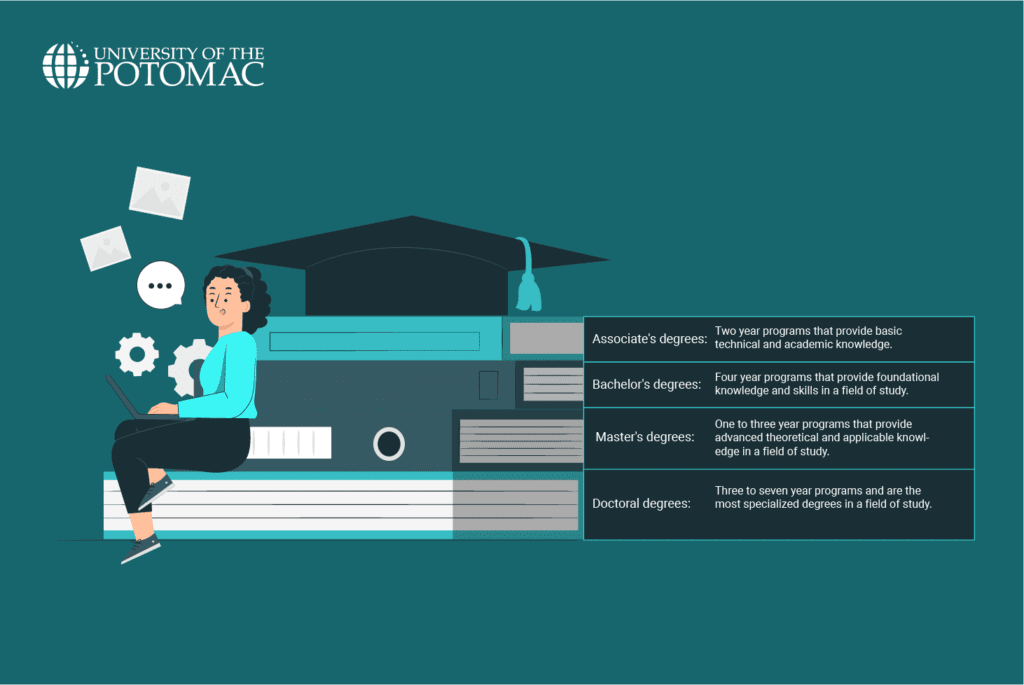
Associate Degrees
An associate degree is a two-year degree awarded by community colleges or technical schools. Some four-year universities, such as UOTP, also offer them.
Associate programs aim to give students the basic technical and academic knowledge and transferable skills needed for employment or further study in their chosen field. Common fields include healthcare, technology, and business.
In terms of level of education, an associate degree falls between high school and a bachelor’s degree. After earning their degree, students can either transfer to a bachelor’s degree or go directly into the workforce.
Bachelor’s Degrees
Bachelor’s degrees are four-year degrees offered by universities and colleges in a specific area of study. The most common types are Bachelor of Arts (BA), Bachelor of Science (BS), Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA), and Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA).
Interested in pursuing a degree?
Fill out the form and get all admission information you need regarding your chosen program.
This will only take a moment.
Message Received!
Thank you for reaching out to us. We will review your message and get right back to you within 24 hours.
If there is an urgent matter and you need to speak to someone immediately you can call at the following phone number:
- We value your privacy.
The structure of bachelor’s degrees encompasses general education courses, core courses, and electives. General education courses are meant to broaden overall knowledge and sharpen transferable skills like communication, critical thinking, and problem-solving. On the other hand, core courses and electives provide foundational subject knowledge that can be applied in a career path.
Graduate Education
Graduate degrees are advanced degrees that provide specialized knowledge and skills in a specific area of study. The most common graduate degrees are master’s and doctoral degrees.
Master’s degrees are graduate degrees that allow students to build advanced theoretical and applied knowledge. They typically take one to three years to complete. Common types of master’s degrees include Master of Arts (MA), Master of Science (MS), and Master of Business Administration (MBA).
On the other hand, doctoral degrees are the most advanced academic degrees and take three to seven years to complete. Common types of doctoral degrees include Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), Doctor of Education (EdD), and professional doctorates such as Doctor of Medicine (MD) and Doctor of Jurisprudence (JD).
Professional and Specialized Education
In addition to higher education degrees, students can also earn professional and specialized education in a specific field. Let’s explore this in more detail below.
Regulated Professions
Architecture, law, and medicine programs fall under the regulated professions category, meaning they need specific degrees, such as an MD, JD, or Bachelor of Architecture (BArch). After earning their degree, students must complete an internship or residency. The curriculum often incorporates the licensing process from a regulatory body to help students secure their license and practice in their profession.
Certifications and Licenses
Certifications and licenses are evidence that an individual possesses specialized training in a specific area and meets industry standards. These credentials are often requirements for professional practice in fields like accounting, education, finance, etc. Examples include Certified Public Accountant (CPA), Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA), teaching credentials, etc.
Impact of Education Levels on Career Opportunities
Your education level can significantly impact career opportunities. In general, individuals with higher levels of education have better job prospects. Employers are increasingly looking for candidates with formal training and qualifications. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) data shows that attaining a higher level of education correlates with a greater earning potential and is linked with lower unemployment rates.
Another benefit of education is that it opens doors to career paths in high-demand industries such as STEM and healthcare. A bachelor’s degree is often the minimum educational background, with master’s and doctoral degrees required for more advanced positions.
Emerging Trends in Education
The future of education depends on evolving societal needs, technological advancements, and changing learning paradigms. Emerging trends in education include:
- Distance learning through online or hybrid programs, which offer flexible, accessible, and personalized learning experiences;
- E-learning platforms like Coursera, Udemy, edX, LinkedIn Learning, etc., which offer courses from prestigious universities and industry leaders;
- Alternative education pathways, such as Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs), certification programs, bootcamps, and micro-credentials, which offer skill development opportunities to prepare individuals for work.
Conclusion
Understanding the different levels of education is crucial to recognizing its significance in society. From early childhood education to higher education, each level is vital in shaping individuals’ knowledge and skills.
Now that you have a good grasp of the major levels of education, you know which level you should pursue to fulfill your educational and career goals. Are you wondering what to do after high school or what degree you should pursue? We welcome you to check out our programs, and who knows, you might find the perfect program for you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What are the options for adult learners?
There are many higher education options for adult learners, such as academic or professional degrees and certifications.
What is the importance of accreditation in education?
Accreditation in education is essential to ensure that an educational program or institution can provide quality education. It provides assurance for students, parents, and employers that the program they’re considering meets rigorous standards of quality.